Anti-static agent for electrically conductive silicone rubber with retained color and mechanical performance
TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes make it possible to produce conductive silicones without compromising the mechanical properties or color of final compounds, unlike other anti-static agents such as multi wall carbon nanotubes and carbon black.
TUBALL™ provides the highest conductivity in comparison with other carbon fillers
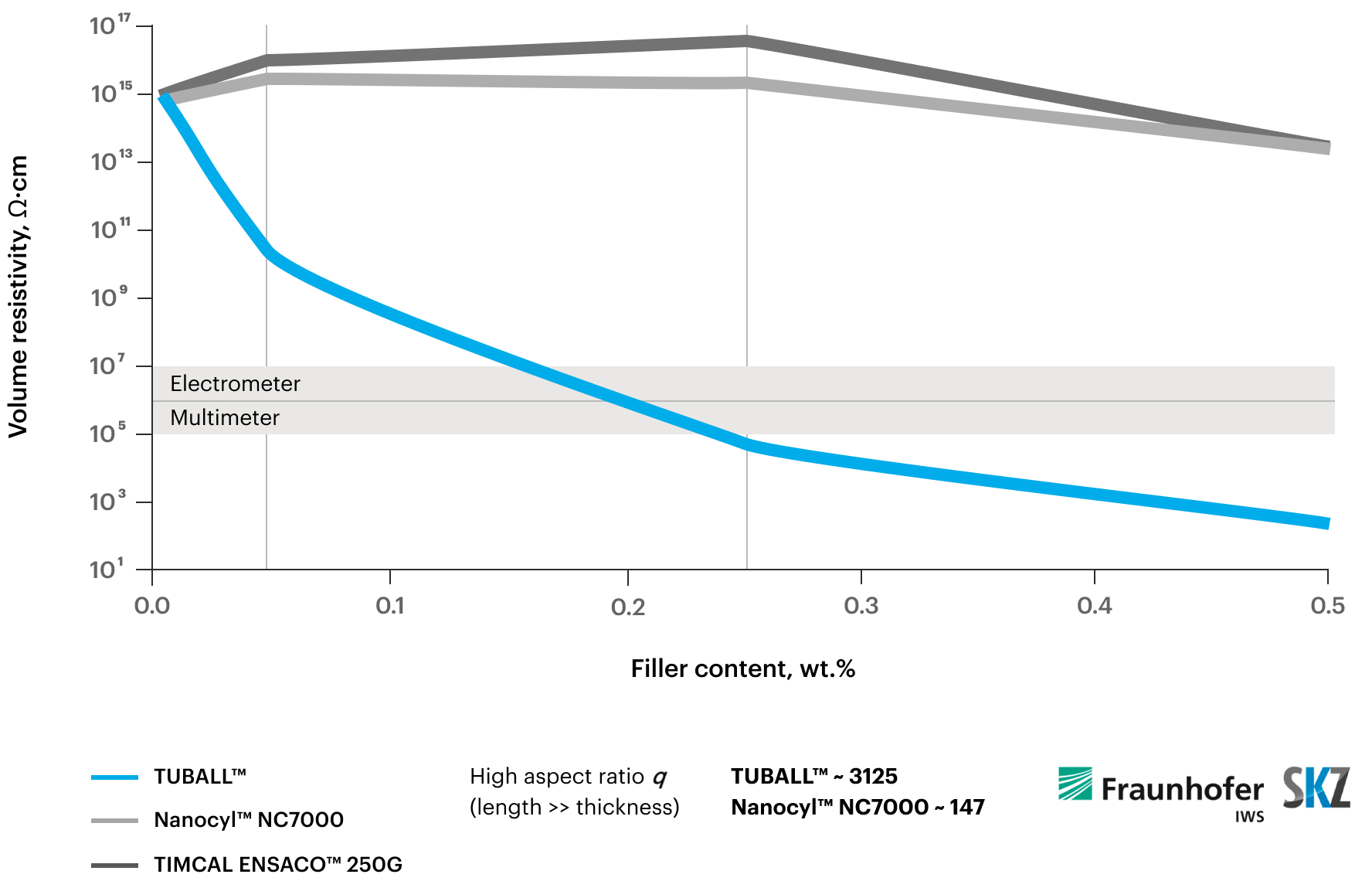
Thanks to their unique properties, such as high conductivity, strength, and flexibility, graphene nanotubes (or single wall carbon nanotubes) form reinforcing conductive networks inside elastomer materials, even at extremely low working dosages. As a result, by switching to graphene nanotubes as an anti-static agent, compounders can obtain materials with required conductive properties, maintained or even improved mechanical properties and color, without dramatic changes in viscosity or production processes.
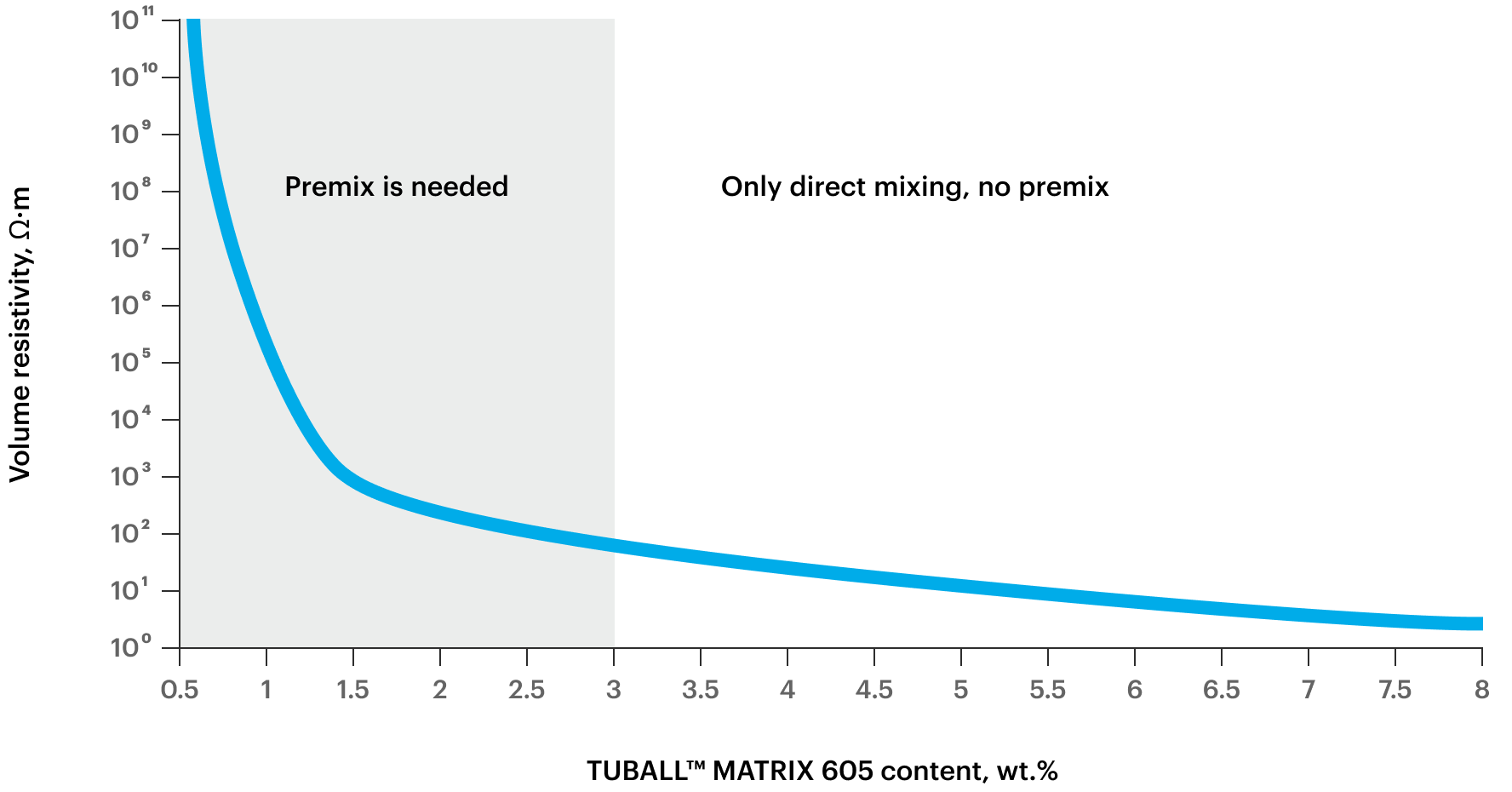
Conductive silicones with TUBALL™ MATRIX
| Currently available | TUBALL™ MATRIX | |
|---|---|---|
| Volume resistivity level | < 100-108 Ω·cm | < 100-108 Ω·cm |
| Concentration of conductive filler | 30-70 wt.% | 0.5-5 wt.% |
| Retain mechanical properties | No | Yes |
| Enable coloration | No | Yes |
FULL RANGE OF RESISTIVITY
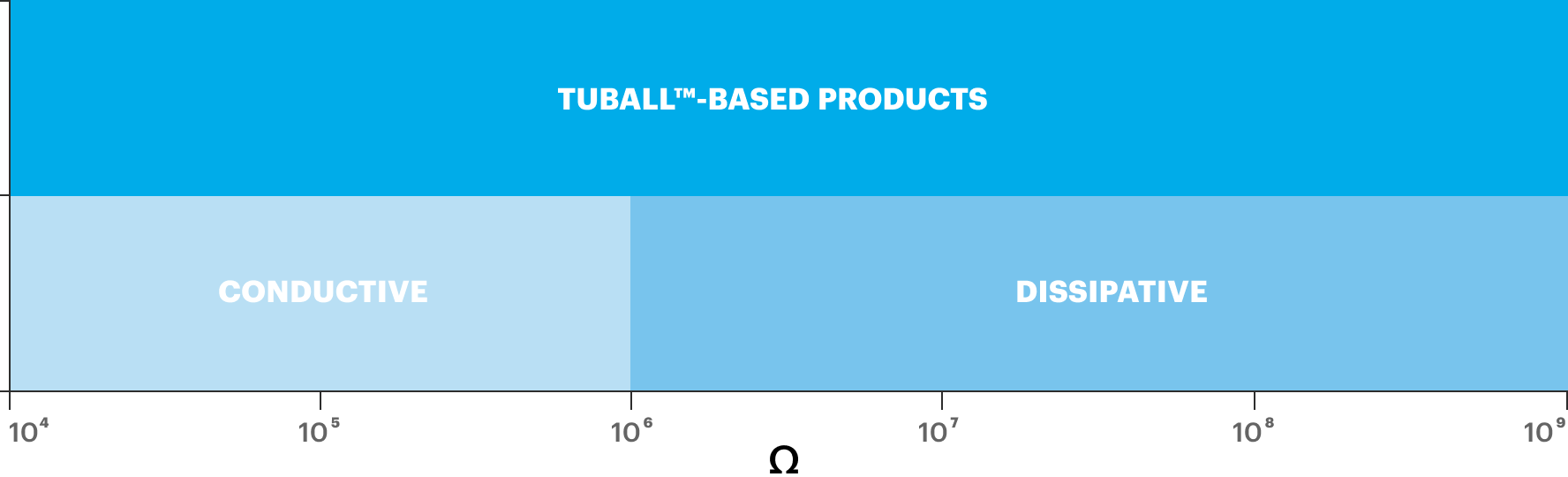
To simplify the handling of nanotubes, OCSiAl has developed TUBALL™ MATRIX concentrates that contain high-quality preliminary dispersed graphene nanotubes. Nanotube concentrates allow good dispersion of nanotubes in anti-static silicone with the application of a standard compounding process. Depending on the antistatic agent concentration in the final compound, the processing conditions, and other system components, the volume resistivity can be adjusted within the range of <10 to 1010 Ω·cm.
Graphene nanotubes are widely applied in fields where silicone compounds require electrical conductivity while maintaining their flexibility, such as in electronics and aerospace as cable accessories and connectors, profiles, gaskets, electrodes, and elements of environmental control systems.
TUBALL™ graphene nanotubes provide to LSR, RTV, and HCR silicones:
- Anti-static, static dissipative, and conductive properties
- Maintained or improved mechanical properties including softness
- Maintained rheology of the uncured compound
- A wide color palette of ESD compounds
- Standard processing and mixing equipment
Currently, OCSiAl offers several varieties of TUBALL™ MATRIX based on different carriers for silicones. Depending on the type of silicone compound, special requirements for resistivity level, and mechanical properties, the appropriate TUBALL™-based concentrate should be used.
To get more details on products, you can click the product cards below, or contact us for assistance in choosing the right nanotube solution.
TUBALL™ for silicones and latexes
| Product | Carrier | Composition | Target systems | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSR | HCR | RTV | PSA (silicone) | NR latex | NBR latex | |||
| TUBALL™ MATRIX concentrates (Black flakes paste @ standard dosage 1.5%–6%) | ||||||||
 | Plasticizer | Polydimethylsiloxane | ||||||
 | Plasticizer | Siloxanes and silicones vinyl group-terminated | ||||||
 | Plasticizer | Siloxanes and silicones vinyl group-terminated | ||||||
 | Plasticizer | Polydimethylsiloxane + zinc chloride (CAS-No. 7646-85-7) + zinc oxide (CAS-No. 1314-13-2) | ||||||
 | Plasticizer | Dimethyl, methylvinyl siloxane | ||||||
| TUBALL™-based suspensions (Black liquid @ standard dosage 0.05–0.1 % of active content in latex) | ||||||||
 | Water + anionic surfactant | Water + anionic surfactant (sodium salt of polynaphthalene sulphonic acid) | ||||||
Related videos
Discover a whole new world inside silicone
Conductive Silicones - LSR, RTV, HCR and PSA
Contact us to discuss your project specifications or to request a TUBALL™ MATRIX sample


